Question 1.
(a) What is a chemical reaction?
(b) State the conditions necessary for a chemical change or reaction.
Solution:
- A chemical reaction is the process of breaking the chemical bonds of the reacting substances (reactants) and making new bonds to form new substances (products).
- Conditions necessary for a chemical change or reaction are
- Evolution of gas
- Change of colour
- Formation of precipitate
- Change of state
Question 2.
Define the following terms
a. Chemical bond
b. Effervescence
c. Precipitate
Solution:
- A chemical bond is the force which holds the atoms of a molecule together as in a compound.
- Formation of gas bubbles in a liquid during a reaction is called effervescence.
- Chemical reactions which are characterised by the formation of insoluble solid substances are called precipitates.
Question 3.
Give an example of a reaction where the following are involved
(a) Heat
(b) Light
(c) Electricity
(d) Close contact
(e) Solution
(f) Pressure
(g) Catalyst
Solution:
Question 4.
Define
(a) Photochemical reaction
(b) Electrochemical reaction
Give an example in each case.
Solution:
Question 5.
Give an example of each of the following chemical changes:
A photochemical reaction involving
(i) silver salt (ii) water
A reaction involving
(i) blue solution
(ii) formation of dirty green precipitate
Two gases combine to form white solid
Two solids combine to form a liquid
A reaction where colour change is noticed
Solution:
Question 6.
Write the chemical reaction where the following changes are observed.
(a) Gas is evolved
(b) Colour change is noticed
(c) Precipitate is formed
(d) Physical state is changed
Solution:
Question 7.
Give reason for the following:
Silver nitrate solution is kept in coloured bottles.
Molybdenum is used in the manufacture of ammonia.
Blue solution of copper sulphate changes to green when a piece of iron is added to this solution.
Colourless concentrated sulphuric acid in a test tube changes to blue on adding a small piece of copper to it.
Solution:
- Silver nitrate solution is kept in brown bottles in the laboratory because it decomposes in the presence of light.
- Molybdenum increases the efficiency of the catalyst iron used in the manufacture of ammonia.
- This is because the blue colour of the copper sulphate solution fades and eventually turns into light green due to the formation of ferrous sulphate.
PAGE NO: 27
Question 1
Complete the following statements:
The chemical change involving iron and hydrochloric acid illustrates a _________________ reaction.
In the type of reaction called_______________, two compounds exchange their positive and negative radicals.
A catalyst either ______ or _____________ the rate of a chemical change but itself remains ______________ at the end of the reaction.
On heating, hydrated copper sulphate changes its colour from ________ to __________.
Solution:
- Displacement
- Double decomposition
- Accelerate, decelerate, unaffected
- Blue, white
Question 2.
When hydrogen burns in oxygen, water is formed; when electricity is passed through water, hydrogen and oxygen are given out. Name the type of chemical change involved in the two cases.
Solution:
Combination
Decomposition
Question 3.
Explain, giving one example for each of the following chemical changes:
(a) Double decomposition
(b) Thermal decomposition
(c) Reversible reaction
(d) Displacement
Solution:
Question 4.
(a) What is synthesis?
(b) What kind of chemical reaction is synthesis? Support your answer by an example.
Solution:
A reaction in which two or more substances combine together to form a single substance is called a synthesis or combination reaction.
A + B → AB
In the above reaction, substances A and B combine to give a molecule of a new substance, AB.
Carbon burns in oxygen to form a gaseous compound, carbon dioxide.
C + O2 → CO2
Question 5.
Decomposition brought about by heat is known as thermal decomposition. What is the difference between thermal dissociation and thermal decomposition?
Solution:
Question 6.
Define neutralization reaction with an example.
Give balanced equation for this reaction.
Give three applications of neutralization reactions.
Solution:
The reaction between an acid and a base which forms salt and water only is referred to as reaction of neutralisation.
Applications of neutralisation reactions:
- When someone is stung by a bee, formic acid enters the skin and causes pain, which can be relieved by rubbing the spot with slaked lime or baking soda, both of which are bases.
- Acid which accidentally spills on to our clothes can be neutralised with ammonia solution.
- If the soil is somewhat acidic and thus unfavourable for growing of certain crops, then slaked lime is added to neutralise the excess acid.
Solution 7:
Hydrolysis is the process in which a salt and water react to form an acidic or basic solution.
In the process of hydrolysis, only those salts hydrolyse which are formed by the reaction of
- strong base and weak acid
- strong acid and weak base
This happens because a salt formed due to a strong base and a weak acid on dissolving in water will form a basic solution.
A basic solution turns red litmus blue.
Na2CO3 + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2CO3
However, the salt formed due to a strong acid and a weak base on dissolving in water will make an acidic solution. Acidic solutions turn blue litmus red.
FeCl3 + 3H2O → Fe(OH)3 + 3HCl
Solution 8:
Iron(III) chloride is a salt prepared from strong acid HCl and a weak base Fe(OH)3.
Fe(OH)3 + 3HCl→ FeCl3 + 3H2O
On the other hand, sodium carbonate is a salt prepared from a strong base NaOH and a weak acid H2CO3.
Fe(OH)3 + 3HCl → FeCl3 + 3H2O
Question 9
(a) What is decomposition?
(b) Support your answer by an example.
Solution:
Decomposition is the breaking up of a compound either into elements or simpler compounds such that these products do not combine to form the original compound.
Decomposition may occur in the presence of heat or light or by the passage of an electric current.
Example: Mercuric oxide when heated decomposes to form two elements-mercury and oxygen.![]()
Question 10.
State the type of reactions each of the following represent and balance the ones that are not balanced.
(a) Cl2 + 2KBr → 2KCl + Br2
(b) NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O
(c) 2HgO → 2Hg + O2
(d) Fe + CuSO4→ FeSO4 + Cu
(e) PbO2 + SO2→ PbSO4
(f) 2KClO3→ 2KCl + 3O2
(g) 2H2O2→ 2H2O + O2
(h) KNO3 + H2SO4 → HNO3 + KHSO4
(i) CuO + H2→ Cu+ H2O
(j) CaCO2→ CaO + CO2
(k) NH4Cl → NH3 + HCl
(l) PbO + 2HNO3→ Pb(NO3) + 2H2O
(m) AgNO3 + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO3
Solution:
- Cl2 + 2KBr → 2KCl + Br2
Displacement - Fe + CuSO4 → FeSO4 + Cu
Displacement - 2H2O → 2Hg + O2
Decomposition - PbO2 + SO2 → PbSO4
Combination - AgNO3 + NaCl → AgCl + NaNO3
Double decomposition - 2KClO3 → 2KCl + 3O2
Decomposition - 2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2
Decomposition - KNO3 + H2SO4 → HNO3 + KHSO4
Double decomposition - CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O
Displacement - CaCO3 → CaO + CO2
Decomposition - NH4Cl → NH3 + HCl
Decomposition
PAGE NO: 30
Question 1.
Explain the main characteristics reactions
Solution:
Define exothermic and endothermic changes. Give two examples in each case.
Solution:

State the effects of endothermic and exothermic reactions on the surroundings.
Solution:
Exothermic reactions are spontaneous and warm their surroundings with the release of heat energy.
Endothermic reactions absorb heat energy from their surroundings and cause their surroundings to cool down.
Give an example of a reaction where the following are involved
(a) Evolution of heat
(b) Absorption of heat
(c) High pressure is required
Solution:

Define:
(a) Photochemical reaction
(b) Electrochemical reaction
Give one example in each case.
Solution:
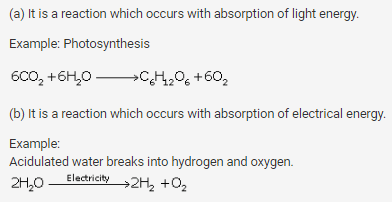
Give an example of each of the following chemical changes.
(a) A reaction involving
(i) Change of state
(b) An exothermic and an endothermic reaction involving carbon as one of the reactants.
(c) A reaction where colour change is noticed.
Solution:

What do you understand by ‘chemical reaction’?
Solution:
A chemical reaction is the process of breaking the chemical bonds of the reacting substances (reactants) and making new bonds to form new substances (products).
A chemical change or chemical reaction occurs when particles collide. Collisions occur when reactants are in close contact or by supply of energy.
Complete and balance the following reactions:
(a) NaCl(aq) + AgNO3(aq) →
(b) Pb(NO3)2 + KI →
(c) CuCO3
(d) Pb(NO3)2
(e) NH3 + O2
Solution:
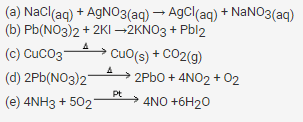
Question 9.
What do you observe? When
- Lead nitrate is heated.
- Silver chloride is exposed to sunlight.
- Hydrogen peroxide is exposed to sunlight.
- H2S gas is passed through copper sulphate solution.
- Barium chloride is added to sodium sulphate solution
- Water is added to the quick lime.
- Sodium chloride solution is added to silver nitrate solution.
Solution:
- Lead nitrate decomposes on heating leaving a yellow residue lead monoxide, brown gas nitrogen dioxide and colourless gas oxygen.
- If chlorine water is exposed to sunlight, oxygen is evolved.
- Hydrogen peroxide breaks down to form water and oxygen gas along with heat energy.
- When hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through a blue solution of copper sulphate, a black precipitate of copper sulphide is obtained and the sulphuric acid so formed remains in the solution.
- A white insoluble precipitate of barium sulphate is formed.
(a) a carbonate which do not decompose on heating.
(b) a nitrate which produces oxygen as the only gas.
(c) a compound which produces carbon dioxide on heating
(d) a nitrate which produces brown gas on heating.
Solution:
- Sodium carbonate
- Sodium nitrate
- Zinc carbonate
- Lead nitrate
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Labels
Class 9 Class 9 Chemistry- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment
This site is all about helping you kids study smart because for Gen Z, studying "hard" is not enough. If you feel there is any way I could improve my posts or if you have any random suggestion that might help make this more kid friendly, please don't hesitate to drop in a comment!
Be sure to check back for my response if you've asked me a question or requested a clarification through the comment section because I do make every effort to reply to your comments here.