Selina ICSE Concise Physics for Class 10 Physics
Chapter 9 Electrical Power and Household Circuits
Exercise 9(A)
1.At what voltage and frequency is the electric power generated at the power generating station?
The electric power is generated at 11 KV, 50Hz at the power generating station.
2.Explain with the aid of a simple diagram, the transmission of electric power from the generating station to your house.
2.Explain with the aid of a simple diagram, the transmission of electric power from the generating station to your house.
Solution 2.
At a power generating station, the electric power is generated at 11 kV. From here, the alternating voltage is transmitted to the grid sub-station and stepped up to 132 kV using a step-up transformer. It is then transmitted to the main sub-station where the voltage is stepped down to 33 kV using a step-down transformer and is then transmitted to the intermediate sub-station. At the intermediate sub-station, the voltage is stepped down to 11 kV using a step-down transformer and is transmitted to the city sub-station, where the voltage is further stepped down to 220 V and is supplied to our houses.
3.
3.
Solution 3.
Electric power from the generating station is transmitted at 11 kV because voltage higher than this causes insulation difficulties, while the voltage lower than this involves high current and loss of energy in form of heat (I2Rt).
4.Explain with the aid of a simple diagram, the transmission of electric power from the generating station to your house.
4.Explain with the aid of a simple diagram, the transmission of electric power from the generating station to your house.
Solution 4.
At 220 V of voltage and 50 Hz of frequency, the a.c. is supplied to our houses.
5.Name the device used to (a) Increase the voltage at the generating station (b) Decrease the voltage at the sub-station for its supply.
5.Name the device used to (a) Increase the voltage at the generating station (b) Decrease the voltage at the sub-station for its supply.
Solution 5.
(a) Step-up transformer
(b) Step-down transformer
6.(a) Name the three connecting wires used in a household circuit.
(b) Which two wires mentioned in part (a) are at the same potential?
(c) In which of the wire stated in part (a) the switch is connected?
6.(a) Name the three connecting wires used in a household circuit.
(b) Which two wires mentioned in part (a) are at the same potential?
(c) In which of the wire stated in part (a) the switch is connected?
Solution 6.
(a) The three connecting wires used in a household circuit are:
- Live (or phase) wire (L),
- Neutral wire (N), and
- Earth wire (E).
(b) Among them neutral and earth wires are at the same potential.
(c) The switch is connected in the live wire.
7.What is the pole fuse? Write down its current rating.
Solution 7.
Before the electric line is connected to the meter in a house, a fuse of rating (≈ 50 A) is connected in the live wire at the pole or just before the meter. This fuse is called the pole fuse.
Its current rating is ≈ 50 A.
8.State the function of each of the following in a house circuiting:
(a) kWh meter,
(b) main fuse, and
(c) main switch.
8.State the function of each of the following in a house circuiting:
(a) kWh meter,
(b) main fuse, and
(c) main switch.
Solution 8.
- After the company fuse, the cable is connected to a kWh meter and from this meter; connections are made to the distribution board through a main fuse and a main switch.
- Main fuse is connected in the live wire and in case of high current it gets burnt and cut the connections to save appliances.
- Main switch is connected in the live and neutral wires. It is used to cut the connections of the live as well as the neutral wires simultaneously from the main supply.
9.In what unit does the electric meter in a house measure the electrical energy consumed? What is its value in S.I. unit?
Solution 9.
The electric meter in a house measures the electrical energy consumed in kWh.
Its value in S.I. unit is 1kWh = 3.6 x 106J.
10.Where is the main fuse connected in a house circuit?
10.Where is the main fuse connected in a house circuit?
Solution 10.
The main fuse in a house circuit is connected on the distribution board, in live wire before the main switch.
11.Draw a circuit diagram to explain the ring system of house wiring. State two advantages of it.
11.Draw a circuit diagram to explain the ring system of house wiring. State two advantages of it.
Solution 11.
- In a ring system the wiring is cheaper than tree system.
- In ring system the sockets and plugs of same size can be used while in a tree system sockets and plugs are of different size.
- In ring system, each appliance has a separate fuse due to which if there is a fault and the fuse of one appliance burns it does not affect other appliances; while in a tree system when fuse in one distribution line blows, it disconnects all the appliances connected to that distribution circuit.
12.Draw a labelled diagram with necessary switch, regulator etc. to connect a bulb/lamp, a plug socket and a fan with the mains.
In what arrangement are these appliances connected to the mains: series or parallel?
Solution 12.
13.How should the several electric lamps be connected with the main so that the switching on or off in a room has no effect on other lamps?
Solution 13.
All the electrical appliances in a building should be connected in parallel at the mains, each with a separate switch and a separate fuse connected in the live wire so that the switching on or off in a room has no effect on other lamps in the same building.
14.Two sets A and B each of four bulbs are glowing in two separate rooms. When one of the bulbs in set A is fused, the other three bulbs also cease to glow. But in set B, when one bulb fuses, the other bulbs continue to glow.
(i) Explain the difference in the two sets,
(ii) Which set of arrangement is preferred in housing circuit and why?
[Hint : in set A, the bulbs are in series; while in set B, the bulbs are in parallel]
14.Two sets A and B each of four bulbs are glowing in two separate rooms. When one of the bulbs in set A is fused, the other three bulbs also cease to glow. But in set B, when one bulb fuses, the other bulbs continue to glow.
(i) Explain the difference in the two sets,
(ii) Which set of arrangement is preferred in housing circuit and why?
[Hint : in set A, the bulbs are in series; while in set B, the bulbs are in parallel]
Solution 14.
In set A, the bulbs are connected in series. Thus, when the fuse of one bulb blows off, the circuit gets broken and current does not flow through the other bulbs also.
In set B, the bulbs are connected in parallel. Thus, each bulb gets connected to its voltage rating (= 220 V) and even when the fuse of one bulb blows off, others remain unaffected and continue to glow.
1(MCQ).The main fuse is connected in :
(a) Live wire
(b) Neutral wire
(c) Both the live and earth wires
(d) Both earth and the neutral wire.
1(MCQ).The main fuse is connected in :
(a) Live wire
(b) Neutral wire
(c) Both the live and earth wires
(d) Both earth and the neutral wire.
Solution 1 (MCQ).
The main fuse is connected in live wire.
Hint: The main fuse is connected in live wire so that if the current exceeds its rating, the fuse melts and breaks the circuit; thus, preventing the excessive current from flowing into the circuit.
2(MCQ).The electrical appliances in a house are connected in :
(a) Series
(b) Parallel
(c) Either in series or parallel
(d) Both in series and parallel
2(MCQ).The electrical appliances in a house are connected in :
(a) Series
(b) Parallel
(c) Either in series or parallel
(d) Both in series and parallel
Solution 2 (MCQ).
Electrical appliances in a house are connected in parallel.
Hint: On connecting the electrical appliances in parallel, each appliance works independently without being affected whether the other appliance is switched on or off.
3(MCQ).The electric meter in a house records :
(a) Charge
(b) Current
(c) Energy
(d) Power
3(MCQ).The electric meter in a house records :
(a) Charge
(b) Current
(c) Energy
(d) Power
Solution 3 (MCQ).
Energy
Hint: The electric meter in a house records the amount of electrical energy consumed in a house.
Exercise 9(B)
1.What is a fuse? Name the material of fuse. State one characteristic of material used for the fuse.
Solution 1.
An electric fuse is a safety device, which is used to limit the current in an electric circuit. The use of fuse safeguards the circuit and appliances connected in that circuit from being damaged.
An alloy of lead and tin is used as a material of fuse because it has low melting point and high resistivity.
2.Name the device used to protect the electric circuits from overloading and short circuit. On what effect of current does it work?
2.Name the device used to protect the electric circuits from overloading and short circuit. On what effect of current does it work?
Solution 2.
‘Fuse’ is used to protect electric circuits from overloading and short circuiting. It works on heating effect of current.
3.Complete the following sentences:
(a) A fuse is a short piece of wire of high _________ and of material low _________.
(b) A fuse wire is made of an alloy of ________ and ________. If the current in a circuit exceeds the current rating of the fuse wire it _________.
(c)A fuse is connected in ________ with the ________ wire.
(d) Higher the current rating,_______ is the fuse wire.
3.Complete the following sentences:
(a) A fuse is a short piece of wire of high _________ and of material low _________.
(b) A fuse wire is made of an alloy of ________ and ________. If the current in a circuit exceeds the current rating of the fuse wire it _________.
(c)A fuse is connected in ________ with the ________ wire.
(d) Higher the current rating,_______ is the fuse wire.
Solution 3.
(a) A fuse is a short piece of wire of material of high resistance and low melting point.
(b) A fuse wire is made of an alloy of lead and tin. If the current in a circuit rises too high, the fuse wiremelts
(c) A fuse is connected in series with the live wire.
(d) Higher the current rating, Thicker is the fuse wire.
4.Why is the fuse wire fitted in a porcelain casing?
4.Why is the fuse wire fitted in a porcelain casing?
Solution 4.
The fuse wire is fitted in a porcelain casing because porcelain is an insulator of electricity.
5.How is a fuse put in an electric circuit? State the purpose of using a fuse in a circuit.
5.How is a fuse put in an electric circuit? State the purpose of using a fuse in a circuit.
Solution 5.
The fuse wire is stretched between the two metallic terminals T1 and T2 in a porcelain holder (since porcelain is an insulator of electricity). This holder fits into a porcelain socket having two metallic terminals to which the live wires of the circuit are connected. The figure below is showing the fuse arrangement.
A fuse is connected with each electrical appliance to safeguard it from the flow of excessive current through it.
6.Describe with the aid of a diagram some form of a fuse, which is used in the electric lighting circuit of a house. Give two reasons why a fuse must not be replaced by an ordinary copper wire.
Solution 6.
The figure above shows the most common fuse arrangement in which the fuse wire is stretched between the two metallic terminals T1 and T2 in a porcelain holder. This holder fits into a porcelain socket having two metallic terminals to each of which the live wire of the circuit is connected.
A fuse must not be replaced with a copper wire because copper has very low resistivity and high melting point.
7.A fuse is always connected to the live wire of the circuit. Explain the reason.
Solution 7.
The fuse wire is always connected in the live wire of the circuit because if the fuse is put in the neutral wire, then due to excessive flow of current when the fuse burns, current stops flowing in the circuit, but the appliance remains connected to the high potential point of the supply through the live wire. Now if a person touches the appliance, he may get a shock as the person will come in contact with the live wire through the appliance.
8.Two fuse wires are rated 5 A and 20 A. Which of the two is thicker,
8.Two fuse wires are rated 5 A and 20 A. Which of the two is thicker,
Solution 8.
The 20 A fuse wire will be thicker so that its resistance be low.
9.Explain the meaning of the statement 'the current rating of a fuse is 5 A'.
9.Explain the meaning of the statement 'the current rating of a fuse is 5 A'.
Solution 9.
It means that the line to which this fuse is connected has a current carrying capacity of 5 A.
10.'A fuse is rated 8 A'. Can it be used with an electrical appliance of rating 5 kW, 200 V?
10.'A fuse is rated 8 A'. Can it be used with an electrical appliance of rating 5 kW, 200 V?
Solution 10.
The safe limit of current which can flow through the electrical appliance is I = P/V = 5000/200 = 25 A; which is greater than 8 A. So, such fuse cannot be used.
11.An electric kettle is rated 3 kW, 250 V. Give reason whether this kettle can be used in a circuit which contains a fuse of current rating 13 A.
11.An electric kettle is rated 3 kW, 250 V. Give reason whether this kettle can be used in a circuit which contains a fuse of current rating 13 A.
Solution 11.
12.(a) What is the purpose of a switch in a circuit?
(b) Why is the switch put in the live wire?
(c) What precaution do you take while handling a switch?
Solution 12.
A switch is an on-off device for current in a circuit (or in an appliance). The switch should always be connected in the live wire so that the appliance could be connected to the high potential point through the live wire. In this position the circuit is complete as the neutral wire provides the return path for the current. When the appliance does not work i.e., in off position of the switch, the circuit is incomplete and no current reaches the appliance.
On the other hand, if switch is connected in the neutral wire, then in ‘off’ position, no current passes through the bulb. But the appliance remains connected to the high potential terminal through the live wire.
Thus, if the switch is connected in the neutral wire, it can be quite deceptive and even dangerous for the user.
Precaution while handling a switch: A switch should not be touched with wet hands.
13.(a) A switch is not touched with wet hands while putting it on or off. Give a reason for your answer.
(b) Name the wire to which a switch is connected.
13.(a) A switch is not touched with wet hands while putting it on or off. Give a reason for your answer.
(b) Name the wire to which a switch is connected.
Solution 13.
A switch should not be touched with wet hands. If water reaches the live wire, it forms a conducting layer between the hand and the live wire of the switch through which the current passes to the hand and the person may get a fatal shock.
14.Draw a circuit diagram using the dual control switches to light a staircase electric light and explain its working.
14.Draw a circuit diagram using the dual control switches to light a staircase electric light and explain its working.
Solution 14.
Let a switch S1 be fitted at the bottom and a switch S2 at the top of the staircase. Fig. (a) shows the off position of the bulb.
The bulb can now be switched on independently by either the switch S1 or the switch S2. If the switch S1 is operated, the connection ‘ab’ is changed to ‘bc’, which completes the circuit and the bulb lights up [Fig. (b)].
Similarly, on operating the switch S2, the connection ‘bc’ changes to ‘ba’, which again completes the circuit [Fig. (c)].
Similarly if the bulb is in on position as shown in Fig. (b) or (c), one can switch off the bulb either from the switch S1 or the switch S2.
15.Draw a circuit diagram using the dual control switches to light a staircase electric light and explain its working.
15.Draw a circuit diagram using the dual control switches to light a staircase electric light and explain its working.
Solution 15.
All electrical appliances are provided with a cable having a plug at one end to connect the appliance to the electric supply.
In this three way pin plug, the top pin is for earthing (E), the live pin (L) in on the left and the neutral pin (N) is on the right.
16.The diagram in fig. shows a three pin plug.
Label the three pins.
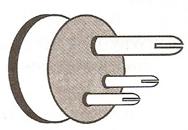
(a) Why is top pin thicker and longer than the other two?
(b) Why are the pins splitted at the ends?
Solution 16.
The three pins in the plug are labelled as
Here E signifies the earth pin,
L is for live wire, and
N is for neutral wire.
- The earth pin is made long so that the earth connection is made first. This ensures the safety of the user because if the appliance is defective, the fuse will blow off. The earth pin is thicker so that even by mistake it cannot be inserted into the hole for the live or neutral connection of the socket.
- The pins are splitted at the end to provide spring action so that they fit in the socket holes tightly.
17.Draw a labelled diagram of a three pin socket.
Solution 17.
18.The diagram in Fig. shows a three-pin socket marked as 1, 2 and 3.
(a)Identify and write live (L), neutral (N) and earth (E) against the correct number.
(b)To which part of the appliance is the terminal 1 connected?
(c)To which wire joined to 2 or 3, is the fuse connected and why?
Solution 18.
(a) 1 – Earth, 2 – Neutral, 3 – Live
(b) Terminal 1 is connected to the outer metallic case of the appliance.
(c) The fuse is connected to live wire joined to 3 so that in case of excessive flow of current fuse melts first and breaks down the circuit to protect appliances.
19.What do you mean by the term local earthing? Explain how it is done
19.What do you mean by the term local earthing? Explain how it is done
Solution 19.
Local earthing is made near kWh meter. In this process a 2 – 3 metre deep hole is dug in the ground. A copper rod placed inside a hollow insulating pipe, is put in the hole. A thick copper plate of dimensionsis 50 cm x 50 cm welded to the lower end of the copper rod and it is buried in the ground. The plate is surrounded by a mixture of charcoal and salt to make a good earth connection.
To keep the ground damp, water is poured through the pipe from time to time. This forms a conducting layer between the plate and the ground. The upper end of the copper rod is joined to the earth connection at the kWh meter.
20.To which wire is the metallic case of an electric appliance connected? give the reason?
20.To which wire is the metallic case of an electric appliance connected? give the reason?
Solution 20.
If the live wire of a faulty appliance comes in to direct contact with the metallic case due to some reason then the appliance acquires the high potential of live wire. This may results in shock if any person touches the body of appliance. But if the appliance is earthed then as soon as the live wire comes in to contact with the metallic case, high current flows through the case to the earth. The fuse connected to the appliance will also blows off, so the appliance get disconnected.
21.(a) The earthing of an electric appliance is useful only if the fuse is in the live wire. Given the reason.
(b) Name the part of the appliance which is earthed.
21.(a) The earthing of an electric appliance is useful only if the fuse is in the live wire. Given the reason.
(b) Name the part of the appliance which is earthed.
Solution 21.
(a) The fuse must be connected in the live wire only. If the fuse is in the neutral wire, then although the fuse burns due to the flow of heavy current, but the appliance remains at the supply voltage so that on touching the appliance current flows through the appliance to the person touching it.
(b) Metallic case of the appliance should be earthed.
22.For earthing an electrical appliance, one has to remove the paint from the metal body of the appliance where the electrical contact is made. Explain the reason.
22.For earthing an electrical appliance, one has to remove the paint from the metal body of the appliance where the electrical contact is made. Explain the reason.
Solution 22.
The paint provides an insulating layer on the metal body of the appliance. To make earth connection therefore, the paint must be removed from the body part where connection is to be made.
23.What is the colour code for the insulation on (a) live, (b) neutral and (c) earth wire?
23.What is the colour code for the insulation on (a) live, (b) neutral and (c) earth wire?
Solution 23.
- According to new international convention
- Live wire is brown in colour.
- Neutral is light blue and
- Earth wire is yellow or green in colour.
24.A power circuit uses a cable using three different wires.
(a) Name the three wires of the cable.
(b)To which of the two wires should the heating element of an electric geyser be connected?
(c)To which wire should the metal case of the geyser be connected?
(d)To which wire should the switch and fuse be connected?
Solution 24.
(a) The three wires are: Live wire, Earth wire and Neutral wire.
(b) The heating element of geyser should be connected to live wire and neutral wire.
(c) The metal case should be connected to earth wire.
(d) The switch and fuse should be connected to live wire.
25.State two circumstances when one may get an electric shock from an electrical gadget. What preventive measures must be provided with the gadget to avoid it?
25.State two circumstances when one may get an electric shock from an electrical gadget. What preventive measures must be provided with the gadget to avoid it?
Solution 25.
One may get an electric shock from an electrical gadget in the following two cases:
1. If the fuse is put in the neutral wire instead of live wire and due to fault, if an excessive current flows in the circuit, the fuse burns, current stops flowing in the circuit but the appliance remains connected to the high potential point of the supply through the live wire. In this situation, if a person touches the faulty appliance, he may get an electric shock as the person will come in contact with the live wire through the appliance.
Preventive measure: The fuse must always be connected in the live wire.
2. When the live wire of a faulty appliance comes in direct contact with its metallic case due to break of insulation after constant use (or otherwise), the appliance acquires the high potential of the live wire. A person touching it will get a shock because current flows through his body to earth.
Preventive measure: Proper ‘earthing’ of the electric appliance should be done.
26.Why is it necessary to have an earth wire installed in a power circuit, but not in a lighting circuit?
26.Why is it necessary to have an earth wire installed in a power circuit, but not in a lighting circuit?
Solution 26.
Power circuit carries high power and costly devices. If there is some unwanted power signal (noise) in the wire it can damage the device. To reduce this effect earth is necessary.
Lighting circuit carries low power (current).So, we ignore the earth terminal.
27.Give two characteristics of a high tension wire.
27.Give two characteristics of a high tension wire.
Solution 27.
A high tension wire has a low resistance and large surface area.
28.Which of the cables, one rated 5 A and the other 15 A will be of thicker wire? Give a reason for your answer.
28.Which of the cables, one rated 5 A and the other 15 A will be of thicker wire? Give a reason for your answer.
Solution 28.
To carry larger current, the resistance of the wire should be low, so its area of cross section should be large. Therefore 15 A current rated wire will be thicker.
29.The diagram in Fig. shows three lamps and three switches 1, 2 and 3.
(a) Name the switch/switches to be closed so as to light all the three lamps.
(b) How are the lamps connected: in series or in parallel?
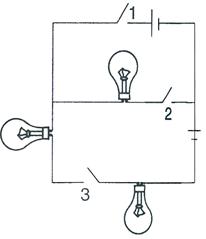
29.The diagram in Fig. shows three lamps and three switches 1, 2 and 3.
(a) Name the switch/switches to be closed so as to light all the three lamps.
(b) How are the lamps connected: in series or in parallel?

Solution 29.
(a) Switches 2 and 3.
(b) The lamps are connected in series.
30.Fig. below shows two bulbs with switches and fuse connected to mains through a socket.
(a) Label each component.
(b) Name and state the colour of insulation of each wire 1, 2 and 3.
(c) How are the two bulbs joined: in series or in parallel?
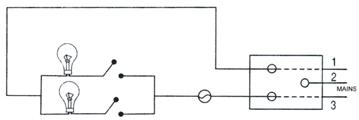
30.Fig. below shows two bulbs with switches and fuse connected to mains through a socket.
(a) Label each component.
(b) Name and state the colour of insulation of each wire 1, 2 and 3.
(c) How are the two bulbs joined: in series or in parallel?

Solution 30.
(a)
(b)
(c) The bulbs are joined in parallel.
1(MCQ).The rating of a fuse connected in the lighting circuit is :
(a) 15 A
(b) 5 A
(c) 10 A
(d) Zero
1(MCQ).The rating of a fuse connected in the lighting circuit is :
(a) 15 A
(b) 5 A
(c) 10 A
(d) Zero
Solution 1 (MCQ).
5 A
Hint: The electric wiring for light and fan circuit uses a thin fuse of low current rating (= 5 A) because the line wire has a current carrying capacity of 5 A.
2(MCQ).A switch must be connected in :
(a) Live wire
(b) Neutral wire
(c) Earth wire
(d) Either earth or neutral wire
2(MCQ).A switch must be connected in :
(a) Live wire
(b) Neutral wire
(c) Earth wire
(d) Either earth or neutral wire
Solution 2 (MCQ).
A switch must be connected in live wire.
Explanation: A switch must be connected in live wire, so that when it is in ‘off’ position, the circuit is incomplete and no current reaches the appliance through the live wire.
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Labels
Class 10 ICSE Physics
Labels:
Class 10
ICSE Physics
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

















This comment has been removed by a blog administrator.
ReplyDeleteThanks. Glad you found it useful 😊
Delete