Selina Concise Chemistry Class 10 ICSE Solutions Mole Concept and Stoichiometry
Exercise 5(A)
1.State :
(a) Gay-Lussac's Law of combining volumes.
(b) Avogadro's law
(a) Gay-Lussac's Law of combining volumes.
(b) Avogadro's law
(a) Gay-Lussac’s law states that when gases react, they do so in volumes which bear a simple ratio to one another, and to the volume of the gaseous product, provided that all the volumes are measured at the same temperature and pressure.
(b) Avogadro’s law states that equal volumes of all gases under similar conditions of temperature and pressure contain the same number of molecules.
2.(a) Define atomicity of a gas. State the atomicity of Hydrogen, Phosphorus and Sulphur.
(b) Differentiate between N2 and 2N.
Solution 2.
a) The number of atoms in a molecule of an element is called its atomicity. Atomicity of Hydrogen is 2, phosphorus is 4 and sulphur is 8.
b) N2means 1 molecule of nitrogen and 2N means two atoms of nitrogen.N2 can exist independently but 2N cannot exist independently.
3.Explain Why?
(a) "The number of atoms in a certain volume of hydrogen is twice the number of atoms in the same volume of helium at the same temperature and pressure."
(b) "When stating the volume of a gas, the pressure and temperature should also be given."
(c)Inflating a balloon seems to violate Boyle's law.
(a) This is due to Avogadros Law which states Equal volumes of all gases under similar conditions of temperature and pressure contain the same number of molecules.
Now volume of hydrogen gas =volume of helium gas
n molecules of hydrogen =n molecules of helium gas
nH2=nHe
1 mol. of hydrogen has 2 atoms of hydrogen and I molecule of helium has 1 atom of helium
Therefore 2H=He
Therefore atoms in hydrogen is double the atoms of helium.
(b) For a given volume of gas under given temperature and pressure, a change in any one of the variable i.e., pressure or temperature changes the volume.
(c) Inflating a balloon seems violating Boyles law as volume is increasing with increase in pressure. Since the mass of gas is also increasing.
4.200 cm3 of hydrogen and 150 cm3 of oxygen are mixed and ignited, as per the following reaction,
2H2 + O2 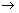 2H2O
2H2O
What volume of oxygen remains unreacted?
Solution 4.
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O
2 V 1V 2V
From the equation, 2V of hydrogen reacts with 1V of oxygen
so 200cm3 of Hydrogen reacts with = 200/2= 100 cm3
Hence, the unreacted oxygen is 150 – 100 = 50cm3 of oxygen.
5.
Solution 5.
6.What volume of oxygen would be required to burn completely 400 ml of acetylene [C2H2]? Also calculate the volume of carbon dioxide formed.
2C2H2 + 5O2 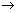 4CO2 + 2H2O (l)
4CO2 + 2H2O (l)
Solution 6.
7.112 cm3 of H2S(g) is mixed with 120 cm3 of Cl2(g) at STP to produce HCl(g) and sulphur(s). Write a balanced equation for this reaction and calculate (i) the volume of gaseous product formed (ii) composition of the resulting mixture.
Solution 7.
8.
Solution 8.
9.What volume of oxygen at STP is required to affect the combustion of 11 litres of ethylene [C2H4] at 273o C and 380 mm of Hg pressure?
C2H4+3O2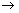 2CO2 + 2H2O
2CO2 + 2H2O
Solution 9.
10.Calulate the volume of HCl gas formed and chlorine gas required when 40 ml of methane reacts completely with chlorine at S.T.P.
CH4 + 2Cl2 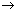 CH2Cl2+2HCl
CH2Cl2+2HCl
Solution 10.
11.What volume of propane is burnt for every 500 cm3 of air used in the reaction under the same conditions? (assuming oxygen is 1/5th of air)
C3H8 + 5O2 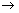 3CO2 + 4H2O
3CO2 + 4H2O
Solution 11.
C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
1 V 5 V 3 V
From equation, 5 V of O2 required = 1V of propane
so, 100 cm3 of O2 will require = 20 cm3 of propane
12.450 cm3 of nitrogen monoxide and 200 cm3 of oxygen are mixed together and ignited. Caclulate the composition of resulting mixture.
2NO + O2 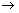 2NO2
2NO2
Solution 12.
13.
Solution 13.
2CO + O2 → 2CO2
2 V 1 V 2 V
2 V of CO requires = 1V of O2
so, 100 litres of CO requires = 50 litre of O2
14.Ammonia may be oxidised to nitrogen monoxide in the presence of a catalyst according to the following equation.
4NH3 + 5O2 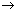 4NO + 6H2O
4NO + 6H2O
If 27 litres of reactants are consumed, what volume of nitrogen monoxide is produced at the same temperature and pressure?
Solution 14.
15.A mixture of hydrogen and chlorine occupying 36 cm3 was exploded. On shaking it with water, 4cm3 of hydrogen was left behind. Find the composition of the mixture.
Solution 15.
H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl
1V 1V 2 V
Since 1 V hydrogen requires 1 V of oxygen and 4cm3 of H2 remained behind so the mixture had com”>16 cm3 hydrogen and 16 cm3 chlorine.
Therefore Resulting mixture is H2 =4cm3,HCl=32cm316.What volume of air (containing 20% O2 by volume) will be required to burn completely 10 cm3 each of methane and acetylene?
CH4 + 2O2 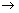 CO2 + 2H2O
CO2 + 2H2O
2C2H2 + 5O2 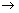 4CO2 + 2H2O
4CO2 + 2H2O
Solution 16.
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
1 V 2 V 1 V
2C2H2 + 5O2 → 4CO2 + 2H2O
2 V 5 V 4 V
From the equations, we can see that
1V CH4 requires oxygen = 2 V O2
So, 10cm3 CH4 will require =20 cm3 O2
Similarly 2 V C2H2 requires = 5 V O2
So, 10 cm3 C2H2 will require = 25 cm3 O2
Now, 20 V O2 will be present in 100 V air and 25 V O2 will be present in 125 V air ,so the volume of air required is 225cm3
17.LPG has 60% propane and 40% butane: 10 litres of this mixture is burnt. Calculate the volume of carbon dioxide added to atmosphere.
C3H8 + 5O2 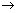 3CO2 + 4H2O
3CO2 + 4H2O
2C4H10 + 13O2 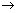 8CO2 + 10H2O
8CO2 + 10H2O
Solution 17.
18.200 cm3 of CO2 is collected at S.T.P when a mixture of acetylene and oxygen is ignited. Calculate the volume of acetylene and oxygen at S.T.P. in original mixture.
2C2H2(g) + 5O2(g) 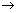 4CO2(g)+ 2H2O(g)
4CO2(g)+ 2H2O(g)
Solution 18.
19.24 cc Marsh gas (CH4) was mixed with 106 cc oxygen and then exploded. On cooling the volume of the mixture became 82 cc, of which, 58 cc was unchanged oxygen. Which law does this experiment support? Explain with calculation.
Solution 19.
This experiment supports Gay lussac’s law of combining volumes.
Since the unchanged or remaining O2 is 58 cc so, used oxygen 106 – 58 = 48cc
According to Gay lussac’s law, the volumes of gases reacting should be in a simple ratio.
CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O
1 V 2 V
24 cc 48 cc
i.e. methane and oxygen react in a 1:2 ratio.
20.You have collected (a) 2 litres of CO2 (b) 3 litres of chlorine (c) 5 litres of hydrogen (d) 4 litres of nitrogen and (e) 1 litres of SO2, under similar conditions of temperature and pressure. Which gas sample will have :
(a) the greatest number of molecules, and
(b) The least number of molecules?
Justify your answers.
Solution 20.
According to Avogadro’s law, equal volumes of gases contain equal no. of molecules under similar conditions of temperature and pressure. This means more volume will contain more molecules and least volume will contain least molecules.
So,(a) 5 litres of hydrogen has greatest no. of molecules with the maximum volume.
(b) 1 litre of SO2 contains the least number of molecules since it has the smallest volume.
21.The gases chlorine, nitrogen, ammonia and sulphur dioxide are collected under the same conditions of temperature and pressure. The following table gives the volumes of gases collected and the number of molecules (x) in 20 litres of nitrogen. You are to complete the table giving the number of molecules in the other gases in terms of x.
Gas | Volume (in litres) | Number of molecules |
Chlorine Nitrogen Ammonia Sulphur dioxide | 10 20 20 5 | x |
Solution 21.
22.
Solution 22.
Exercise 5(B)
1.(a) The relative atomic mass of Cl atom is 35.5 a.m.u. Explain this statement.
(b) What is the value of Avogadro's number?
(c) What is the value of molar volume of a gas at S.T.P?
Solution 1.
a) This statement means one atom of chlorine is 35.5 times heavier than 1/12 time of the mass of an atom C-12.
b) The value of avogadro’s number is 6.023 × 1023c) The molar volume of a gas at STP is 22.4 dm3 at STP
2.Define or explain the terms (a) Vapour density
(b) Molar volume
(c) Relative atomic mass
(d) Relative molecular mass
(e) Avogadro's number
(f) Gram atom
(g) Mole
Solution 2.
(a) The vapour density is the ratio between the masses of equal volumes of gas and hydrogen under the conditions of standard temperature and pressure.
(b) Molar volume is the volume occupied by one mole of the gas at STP. It is equal to 22.4 dm3.
(c) The relative atomic mass of an element is the number of times one atom of the element is heavier than 1/12 times of the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
(d) The relative molecular mass of an compound is the number that represents how many times one moleculae of the substance is heavier than 1/12 of the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
(e) The number of atoms present in 12g (gram atomic mass) of C-12 isotope, i.e. 6.023 x1023 atoms.
(f) The quantity of the element which weighs equal to its gram atomic mass is called one gram atom of that element.
(g) Mole is the amount of a substance containing elementary particles like atoms, molecules or ions in 12 g of carbon-12.
3.(a) What are the main applications of Avogadro's Law?
(b) How dose Avogadro's Law explain Gay-Lussac's Law of combining volumes?
Solution 3.
(a) Applications of Avogadro’s Law :
- It explains Gay-Lussac’s law.
- It determines atomicity of the gases.
- It determines the molecular formula of a gas.
- It determines the relation between molecular mass and vapour density.
- It gives the relationship between gram molecular mass and gram molecular volume.
(b) According to Avogadro’s law under the same conditions of temperature and pressure, equal volumes of different gases have the same number of molecules.
Since substances react in simple ratio by number of molecules, volumes of the gaseous reactants and products will also bear a simple ratio to one another.This what Gay Lussac’s Law says.
H2 + Cl2 → 2HCl1V 1V 2V (By Gay-Lussacs law)
n molecules n molecules 2n molecules (By Avogadros law)
4.Calculate the relative molecular masses of:
(a) Ammonium chloroplatinate, (NH4)2 PtCl6
(b) Potassium chlorate (c) CuSO4. 5H2O (d) (NH4)2SO4
(e) CH3COONa (f) CHCl3 (g) (NH4)2 Cr2O7
Solution 4.
(a) (2N)28 + (8H)8 + (Pt)195 + (6Cl)35.5 x 6 = 444
(b) KClO3 = (K)39 + (Cl)35.5 + (3O)48 = 122.5
(c) (Cu)63.5 + (S)32 + (4O)64 + (5H2O)5 x 18 = 249.5
(d) (2N)28 + (8H)8 + (S)32 + (4O)64 = 132
(e) (C)12 + (3H)3 + (C)12 + (2O)32 + (Na)23 = 82
(f) (C)12 + (H)1+ (3Cl)3 x 35.5 = 119.5
(g) (2N)28 + (8H)8 + (2Cr)2 x 51.9+ (7O)7 x 16 = 252
5.Find the
(a) number of molecules in 73 g of HCl,
(b) weight of 0.5 mole of O2,
(c) number of molecules in 1.8 g of H2O
(d) number of moles in 10 g of CaCO3
(e) Weight of 0.2 mole of H2 gas,
(f) Number of molecules in 3.2 g of SO2.
Solution 5.
(a) No. of molecules in 73 g HCl = 6.023 x1023 x 73/36.5(mol. mass of HCl)
= 12.04 x 1023
(b) Weight of 0.5 mole of O2 is = 32(mol. Mass of O2) x 0.5=16 g
(c) No. of molecules in 1.8 g H2O = 6.023 x 1023 x 1.8/18
= 6.023 x 1022
(d) No. of moles in 10g of CaCO3 = 10/100(mol. Mass CaCO3)
= 0.1 mole
(e) Weight of 0.2 mole H2 gas = 2(Mol. Mass) x 0.2 = 0.4 g
(f) No. of molecules in 3.2 g of SO2 = 6.023 x 1023 x 3.2/64
= 3.023 x 1022
6.Which of the following would weigh most?
(a) 1 mole of H2O (b) 1 mole of CO2 (c) 1 mole of NH3 (d) 1 mole of CO
Solution 6.
Molecular mass of H2O is 18, CO2 is 44, NH3 is 17 and CO is 28
So, the weight of 1 mole of CO2 is more than the other three.
7.Which of the following contains maximum number of molecules?
(a) 4 g of O2 (b) 4 g of NH3 (c ) 4 g of CO2 (d) 4 g of SO2
Solution 7.
4g of NH3 having minimum molecular mass contain maximum molecules.
8.Calculate the number of
(a) Particles in 0.1 mole of any substance.
(b) Hydrogen atoms in 0.1 mole of H2SO4.
(c) Molecules in one Kg of calcium chloride.
Solution 8.
a) No. of particles in s1 mole = 6.023 x 1023
So, particles in 0.1 mole = 6.023 x 10 23 x 0.1 = 6.023 x 1022
b) 1 mole of H2SO4 contains =2 x 6.023 x 1023
So, 0.1 mole of H2SO4 contains =2 x 6.023 x 1023 x0.1
= 1.2×1023 atoms of hydrogen
c) 111g CaCl2 contains = 6.023 x 1023 molecules
So, 1000 g contains = 5.42 x 1024 molecules
9.How many grams of
(a) Al are present in 0.2 mole of it?
(b) HCl are present in 0.1 mole of it?
(c) H2O are present in 0.2 mole of it?
(d) CO2 is present in 0.1 mole of it?
Solution 9.
(a) 1 mole of aluminium has mass = 27 g
So, 0.2 mole of aluminium has mass = 0.2 x 27 = 5.4 g
(b) 0.1 mole of HCl has mass = 0.1 x 36.5 (mass of 1 mole)
= 3.65 g
(c) 0.2 mole of H2O has mass = 0.2 x 18 = 3.6 g
(d) 0.1 mole of CO2 has mass = 0.1 x 44 = 4.4 g
10.(a) The mass of 5.6 litres of a certain gas at S.T.P. is 12 g. What is the relative molecular mass or molar mass of the gas?
(b) Calculate the volume occupied at S.T.P. by 2 moles of SO2.
Solution 10.
(a) 5.6 litres of gas at STP has mass = 12 g
So, 22.4 litre (molar volume) has mass =12 x 22.4/5.6
= 48g(molar mass)
(b) 1 mole of SO2 has volume = 22.4 litres
So, 2 moles will have = 22.4 x 2 = 44.8 litre
11.Calculate the number of moles of
(a) CO2 which contain 8.00 g of O2
(b) Methane in 0.80 g of methane.
Solution 11.
(a) 1 mole of CO2 contains O2 = 32g
So, CO2 having 8 gm of O2 has no. of moles = 8/32 = 0.25 moles
(b) 16 g of methane has no. of moles = 1
So, 0.80 g of methane has no. of moles = 0.8/16 = 0.05 moles
12.Calculate the actual mass of
(a) An atom of oxygen (b) an atom of hydrogen
(c) a molecule of NH3 (d) the atom of silver
(e) the molecule of oxygen
(f) 0.25 gram atom of calcium
Solution 12.
(a) 6.023 x 10 23 atoms of oxygen has mass = 16 g
So, 1 atom has mass = 16/6.023 x 1023 = 2.656 x 10-23 g
(b) 1 atom of Hydrogen has mass = 1/6.023 x 1023 = 1.666 x 10-24
(c) 1 molecule of NH3 has mass = 17/6.023 x1023 = 2.82 x 10-23 g
(d) 1 atom of silver has mass = 108/6.023 x 1023 =1.701 x 10-22
(e) 1 molecule of O2 has mass = 32/6.023 x 1023 = 5.314 x 10-23 g
(f) 0.25 gram atom of calcium has mass = 0.25 x 40 = 10g
13.Calculate the mass of 0.1 mole of each of the following
(a) CaCO3 (b) Na2SO4.10H2O
(c) CaCl2 (d) Mg
(Ca = 40, Na=23, Mg =24, S=32, C = 12, Cl = 35.5, O=16, H=1)
Solution 13.
(a) 0.1 mole of CaCO3 has mass =100(molar mass) x 0.1=10 g
(b) 0.1 mole of Na2SO4.10H2O has mass = 322 x 0.1 = 32.2 g
(c) 0.1 mole of CaCl2 has mass = 111 x 0.1 = 11.1g
(d) 0.1 mole of Mg has mass = 24 x 0.1 = 2.4 g
14.Calculate the number of
oxygen atoms in 0.10 mole of Na2CO3.10H2O.
Solution 14.
1molecule of Na2CO3.10H2O contains oxygen atoms = 13
So, 6.023 x1023 molecules (1mole) has atoms=13 x 6.023 x 1023
So, 0.1 mole will have atoms = 0.1 x 13 x 6.023 x 1023 =7.8 x 1023
15.What mass of Ca will contain the same number of atoms as are present in 3.2 g of S?
Solution 15.
3.2 g of S has number of atoms = 6.023 x1023 x 3.2 /32
= 0.6023 x 1023
So, 0.6023 x 1023 atoms of Ca has mass=40 x0.6023×1023/6.023 x 1023
= 4g
16.Calculate the number of atoms in each of the following:
(a) 52 moles of He (b) 52 amu of He (c ) 52 g of He
Solution 16.
(a) No. of atoms = 52 x 6.023 x1023 = 3.131 x 1025
(b) 4 amu = 1 atom of He
so, 52 amu = 13 atoms of He
(c) 4 g of He has atoms = 6.023 x1023
So, 52 g will have = 6.023 x 1023 x 52/4 = 7.828 x1024 atoms
17.Calculate the number of atoms of each kind in 5.3 grams of sodium carbonate.
Solution 17.
Molecular mass of Na2CO3 = 106 g
106 g has 2 x 6.023 x1023 atoms of Na
So, 5.3g will have = 2 x 6.023 x1023x 5.3/106=6.022 x1022 atoms
Number of atoms of C = 6.023 x1023 x 5.3/106 = 3.01 x 1022 atoms
And atoms of O = 3 x 6.023 x 1023 x 5.3/106= 9.03 x1022 atoms
18.(a) Calculate the mass of nitrogen supplied to soil by 5 kg of urea [CO(NH2)2] [O = 16; N = 14; C = 12 ; H = 1 ]
(b) Calculate the volume occupied by 320 g of sulphur dioxide at S.T.P. [S = 32; O = 16]
Solution 18.
(a) 60 g urea has mass of nitrogen(N2) = 28 g
So, 5000 g urea will have mass = 28 x 5000/60 = 2.33 kg
(b) 64 g has volume = 22.4 litre
So, 320 g will have volume = 22.4 x 320/64=112 litres
19.(a) What do you understand by the statement that 'vapour density of carbon dioxide is 22'?
(b) Atomic mass of Chlorine is 35.5.What is its vapour density?
Solution 19.
(a) Vapour density of carbon dioxide is 22, it means that 1 molecule of carbon dioxide is 22 heavier than 1 molecule of hydrogen.
(b) Vapour density of Chlorine atom is 35.5.
20.What is the mass of 56 cm3 of carbon monoxide at STP?
(C=12 ,O=16)
Solution 20.
22400 cm3 of CO has mass = 28 g
So, 56 cm3 will have mass = 56 x 28/22400 = 0.07 g
21.Determine the number of molecules in a drop of water which weighs 0.09g.
Solution 21.
18 g of water has number of molecules = 6.023 x 1023
So, 0.09 g of water will have no. of molecules = 6.023 x 1023 x 0.09/18 = 3.01 x 1021 molecules
22.The molecular formula for elemental sulphur is S8.In sample of 5.12 g of sulphur
(a) How many moles of sulphur are present?
(b) How many molecules and atoms are present?
Solution 22.
(a) No. of moles in 256 g S8 = 1 mole
So, no. of moles in 5.12 g = 5.12/256 = 0.02 moles
(b) No. of molecules = 0.02 x 6.023 x 1023 = 1.2 x 1022 molecules
No. of atoms in 1 molecule of S = 8
So, no. of atoms in 1.2 x 1022 molecules = 1.2 x 1022 x 8
= 9.635x 1022 molecules
23.If phosphorus is considered to contain P4 molecules, then calculate the number of moles in 100g of phosphorus?
Solution 23.
Atomic mass of phosphorus P = 30.97 g
Hence, molar mass of P4 = 123.88 g
If phosphorus is considered as P4 molecules,
then 1 mole P4 ≡ 123.88 g
Therefore, 100 g of P4 = 0.807 g
24.Calculate:
(a) The gram molecular mass of chlorine if 308cm3 of it at STP weighs 0.979 g
(b) The volume of 4g of H2 at 4 atmospheres.
(c) The mass of oxygen in 2.2 litres of CO2 at STP.
Solution 24.
25.A student puts his signature with graphite pencil. If the mass of carbon in the signature is 10-12 g, calculate the number of carbon atoms in the signature.
Solution 25.
No. of atoms in 12 g C = 6.023 x1023
So, no. of carbon atoms in 10-12 g = 10-12 x 6.023 x1023/12
= 5.019 x 1010 atoms
26.An unknown gas shows a density of 3 g per litre at 2730C and 1140 mm Hg pressure. What is the gram molecular mass of this gas?
Solution 26.
Given:
P= 1140 mm Hg
Density = D = 2.4 g / L
T = 273 0C = 273+273 = 546 K
M = ?
We know that, at STP, the volume of one mole of any gas is 22.4 L
Hence we have to find out the volume of the unknown gas at STP.
First apply Charle’s law.
We have to find out the volume of one liter of unknown gas at standard temperature 273 K.
V1= 1 L T1 = 546 K
V2=? T2 = 273 K
V1/T1 = V2/ T2
V2 = (V1 x T2)/T1
= (1 L x 273 K)/546 K
= 0.5 L
We have found out the volume at standard temperature. Now we have to find out the volume at standard pressure.
Apply Boyle’s law.
P 1 = 1140 mm Hg V1 = 0.5 L
P2 = 760 mm Hg V2 = ?
P1 x V1 = P2 x V2
V2 = (P1 x V1)/P2
= (1140 mm Hg x 0.5 L)/760 mm Hg
= 0.75 L
Now, 22.4 L is the volume of 1 mole of any gas at STP, then 0.75 L is the volume of X moles at STP
X moles = 0.75 L / 22.4 L
= 0.0335 moles
The original mass is 2.4 g
n = m / M
0.0335 moles = 2.4 g / M
M = 2.4 g / 0.0335 moles
M= 71.6 g / mole
Hence, the gram molecular mass of the unknown gas is 71.6 g
27.Cost of Sugar (C12H22 O11) is Rs 40 per kg; calculate its cost per mole.
Solution 27.
1000 g of sugar costs = Rs. 40
So, 342g(molar mass) of sugar will cost=342×40/1000=Rs. 13.68
28.Which of the following weighs the least?
(a) 2 g atom of N (b) 3 x1025 atoms of carbon (c)1mole of sulphur d)7 g of silver
Solution 28.
29.Four grams of caustic soda contains:
(a) 6.02 x 1023 atoms of it
(b) 4 g atom of sodium
(c) 6.02 x1022 molecules
(d) 4 moles of NaOH
Solution 29.
40 g of NaOH contains 6.023 x 1023 molecules
So, 4 g of NaOH contains = 6.02 x1023 x 4/40
= 6.02 x1022 molecules
30.The number of molecules in 4.25 g of ammonia is:
(a) 1.0 x 1023 (b) 1.5 x 1023 (c) 2.0 x 1023 (d) 3.5x 1023
Solution 30.
The number of molecules in 18 g of ammonia= 6.02 x1023
So, no. of molecules in 4.25 g of ammonia = 6.02 x 1023 x 4.25/18
= 1.5 x 1023
31.Correct the statements, if required
(a) One mole of chlorine contains 6.023 x 1010 atoms of chlorine.
(b) Under similar conditions of temperature and pressure, two volumes of hydrogen combined with two volumes of oxygen will give two volumes of water vapour.
(c) Relative atomic mass of an element is the number of times one molecule of an element is heavier than 1/12 the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
(d) Under similar conditions of temperature and pressure, equal volumes of all gases contain the same number of atoms.
Solution 31.
(a) One mole of chlorine contains 6.023 x 1023 atoms of chlorine.
(b) Under similar conditions of temperature and pressure, two volumes of hydrogen combined with one volume of oxygen will give two volumes of water vapour.
(c) Relative atomic mass of an element is the number of times one atom of an element is heavier than 1/12 the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
(d) Under similar conditions of temperature and pressure, equal volumes of all gases contain the same number of molecules.
Exercise 5(C)
1.Give three kinds of information conveyed by the formula H2O.
Solution 1.
Information conveyed by H2O
1. That H2O contains 2 volumes of hydrogen and 1 volume of oxygen.
2. That ratio by weight of hydrogen and oxygen is 1:8.
3. That molecular weight of H2O is 18g.
2.Explain the terms empirical formula and molecular formula.
Solution 2.
The empirical formula is the simplest formula, which gives the simplest ratio in whole numbers of atoms of different elements present in one molecule of the compound.
The molecular formula of a compound denotes the actual number of atoms of different elements present in one molecule of a compound.
3.Give the empirical formula of:
(a) C6H6 (b) C6H12O6 (c) C2H2 (d) CH3COOH
3.Give the empirical formula of:
(a) C6H6 (b) C6H12O6 (c) C2H2 (d) CH3COOH
Solution 3.
(a) CH (b) CH2O (c) CH (d) CH2O
4.
Solution 4.
5.Calculate the percentage of phosphorus in
(a) Calcium hydrogen phosphate Ca(H2PO4)2
(b) Calcium phosphate Ca3(PO4)2
Solution 5.
6.Calculate the percent composition of Potassium chlorate KClO3.
Solution 6.
Molecular mass of KClO3 = 122.5 g
% of K = 39 /122.5 = 31.8%
% of Cl = 35.5/122.5 = 28.98%
% of O = 3 x 16/122.5 = 39.18%
7.Find the empirical formula of the compounds with the following percentage composition:
Pb = 62.5%, N = 8.5%, O = 29.0%
Solution 7.
8.Calculate the mass of iron in 10 kg of iron ore which contains 80% of pure ferric oxide.
Solution 8.
9.If the empirical formula of two compounds is CH and their Vapour densities are 13 to 39 respectively, find their molecular formula.
Solution 9.
10.Find the empirical formula of a compound containing 17.7% hydrogen and 82.3% nitrogen.
Solution 10.
11.On analysis, a substance was found to contain
C = 54.54%, H = 9.09%, O = 36.36%
The vapour density of the substance is 44,calculate;
(a) its empirical formula, and
(b) its molecular formula
Solution 11.
12.An organic compound ,whose vapour density is 45, has the following percentage composition
H=2.22%, O = 71.19% and remaining carbon. Calculate ,
(a) its empirical formula, and
(b) its molecular formula
Solution 12.
13.An organic compound contains H = 4.07%, Cl = 71.65% chlorine and remaining carbon. Its molar mass = 98.96. Find,
(a) Empirical formula, and
(b) Molecular formula
Solution 13.
14.A hydrocarbon contains 4.8g of carbon per gram of hydrogen. Calculate
(a) the g atom of each
(b) find the empirical formula
(c) Find molecular formula, if its vapour density is 29.
Solution 14.
15.0.2 g atom of silicon Combine with 21.3 g of chlorine. Find the empirical formula of the compound formed.
Solution 15.
16.
Solution 16.
17.In a compound of magnesium (Mg = 24) and nitrogen (N = 14), 18 g of magnesium combines with 7g of nitrogen. Deduce the simplest formula by answering the following questions.
(a) How many gram- atoms of magnesium are equal to 18g?
(b) How many gram- atoms of nitrogen are equal to 7g of nitrogen?
(c) Calculate simple ratio of gram- atoms of magnesium to gram-atoms of nitrogen and hence the simplest formula of the compound formed.
Solution 17.
(a) G atoms of magnesium = 18/24 = 0.75 or g- atom of Mg
(b) G atoms of nitrogen = 7/14 = 0.5 or 1/2 g- atoms of N
(c) Ratio of gram-atoms of N and Mg = 1:1.5 or 2:3
So, the formula is Mg3 N2
18.Barium chloride crystals contain 14.8% water of crystallization. Find the number of molecules of water of crystallization per molecule.
Solution 18.
Barium chloride = BaCl2.x H2O
Ba + 2Cl + x[H2 + O]
= 137+ 235.5 + x [2+16]
= [208 + 18x] contains water = 14.8% water in BaCl2.x H2O
= [208 + 18 x] 14.8/100 = 18x
= [104 + 9x] 2148=18000x
= [104+9x] 37=250x
= 3848 + 333x =2250x
1917x =3848
x = 2molecules of water
19.Urea is very important nitrogenous fertilizer. Its formula is CON2H4.Calculate the percentage of nitrogen in urea. (C=12,O=16 ,N=14 and H=1).
Solution 19.
Molar mass of urea; CON2H4 = 60 g
So, % of Nitrogen = 28 × 100/60 = 46.66%
20.Determine the formula of the organic compound if its molecule contains 12 atoms of carbon. The percentage compositions of hydrogen and oxygen are 6.48 and 51.42 respectively.
Solution 20.
Element % At. mass Atomic ratio Simple ratio
C 42.1 12 3.5 1
H 6.48 1 6.48 2
O 51.42 16 3.2 1
The empirical formula is CH2O
Since the compound has 12 atoms of carbon, so the formula is
C12 H24 O12.
21.(a) A compound with empirical formula AB2, has the vapour density equal to its empirical formula weight. Find its molecular formula.
(b) A compound with empirical formula AB has vapour density 3 times its empirical formula weight. Find the molecular formula.
Solution 21.
(a) Now since the empirical formula is equal to vapour density and we know that vapour density is half of the molecular mass i.e. we have n=2 so, molecular formula is A2B4.
(b) Since molecular mass is 2 times the vapour density, so Mol. Mass = 2 V.D
Empirical formula weight = V.D/3
So, n = molecular mass/ Empirical formula weight = 6
Hence, the molecular formula is A6B6
22.A hydride of nitrogen contains 87.5% per cent by mass of nitrogen. Determine the empirical formula of this compound.
Solution 22.
Atomic ratio of N = 87.5/14 = 6.25
Atomic ratio of H= 12.5/1 = 12.5
This gives us the simplest ratio as 1:2
So, the molecular formula is NH2
23.A compound has O=61.32%, S= 11.15%, H=4.88% and Zn=22.65%.The relative molecular mass of the compound is 287 amu. Find the molecular formula of the compound, assuming that all the hydrogen is present as water of crystallization.
Solution 23.
Element % at. mass atomic ratio simple ratio
Zn 22.65 65 0.348 1
H 4.88 1 4.88 14
S 11.15 32 0.348 1
O 61.32 16 3.83 11
Empirical formula of the given compound =ZnSH14O11
Empiricala formula mass = 65.37+32+141+11+16=287.37
Molecular mass = 287
n = Molecular mass/Empirical formula mass = 287/287=1
Molecular formula = ZnSO11H14
= ZnSO4.7H2O
Exercise 5(D)
1.Complete the following blanks in the equation as indicated.
CaH2 (s) + 2H2O (aq) 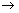 Ca(OH)2 (s) + 2H2 (g)
Ca(OH)2 (s) + 2H2 (g)
(a) Moles: 1 mole + -------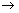 -------- + --------------
-------- + --------------
(b) Grams: 42g + -------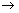 -------- + ----------------
-------- + ----------------
(c) Molecules: 6.02 x 1023 + ------- 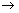 -------- + -----------
-------- + -----------
Solution 1.
2.The reaction between 15 g of marble and nitric acid is given by the following equation:
CaCO3 + 2HNO3  Ca(NO3)2+ H2O + CO2
Ca(NO3)2+ H2O + CO2
Calculate: (a) the mass of anhydrous calcium nitrate formed, (b) the volume of carbon dioxide evolved at S.T.P.
Solution 2.
3.66g of ammounium sulphate is produced by the action of ammonia on sulphuric acid.
Write a balanced equation and calculate:
(a) Mass of ammonia required.
(b) The volume of the gas used at the S.T.P.
(c) The mass of acid required.
Solution 3.
4.The reaction between red lead and hydrochloric acid is given below:
Pb3O4 + 8HCl  3PbCl2 + 4H2O + Cl2
3PbCl2 + 4H2O + Cl2
Calculate: (a) the mass of lead chloride formed by the action of the 6.85 g of red lead, (b) the mass of the chlorine and (c) the volume of the chlorine evolved at S.T.P.
Solution 4.
5.Find the mass of KNO3 required to produce 126 kg of nitric acid. Find whether a larger or smaller mass of NaNO3 is required for the same purpose.
KNO3+ H2SO4  KHSO4 + HNO3
KHSO4 + HNO3
NaNO3 + H2SO4  NaHSO4 + HNO3
NaHSO4 + HNO3
Solution 5.
Molecular mass of KNO3 = 101 g
63 g of HNO3 is formed by = 101 g of KNO3
So, 126000 g of HNO3 is formed by = 126000 x 101/63 = 202 kg
Similarly,126 g of HNO3 is formed by 170 kg of NaNO3
So, smaller mass of NaNO3 is required.
6.Pure calcium carbonate and dilute hydrochloric acid are reacted and 2 litres of carbon dioxide was collected at 27oC and normal pressure.
Calculate :
(a) The mass of salt required.
(b) The mass of the acid required to prepare the 2 litres of CO2 at 27 C and normal pressure.
CaCO3 + 2HCl CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
CaCl2 + H2O + CO2
Solution 6.
7.Calculate the mass and volume of oxygen at S.T.P., which will be evolved on electrolysis of 1 mole (18g) of water
Solution 7.
8.1.56 g of sodium peroxide reacts with water according to the following equation:
2Na2O2 + 2H2O 4NaOH + O2
4NaOH + O2
Calculate:
(a) mass of sodium hydroxide formed,
(b) Volume of oxygen liberated at S.T.P.
(c) Mass of oxygen liberated.
Solution 8.
9.(a) Calculate the mass of ammonia that can be obtained from 21.4 g of NH4Cl by the reaction:
2NH4Cl + Ca(OH)2 CaCl2 +2H2O + 2NH3
CaCl2 +2H2O + 2NH3
(b) What will be the volume of ammonia when measured at S.T.P?
The molar volume of a gas = 22.4 litres at STP.
Solution 9.
10.
Solution 10.
11.MnO2 + 4HCl  MnCl2 + 2H2O +Cl2
MnCl2 + 2H2O +Cl2
0.02 moles of pure MnO2is heated strongly with conc. HCl. Calculate:
(a) mass of MnO2 used
(b) moles of salt formed,
(c) mass of salt formed,
(d) moles of chlorine gas formed,
(e) mass of chlorine gas formed,
(f) volume of chlorine gas formed at S.T.P.,
(g) moles of acid required,
(h) Mass of acid required.
Solution 11.
12.Nitrogen and hydrogen react to form ammonia.
N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) 2NH3 (g)
2NH3 (g)
If 1000g H2 react with 2000g of N2:
(a) Will any of the two reactants remain unreacted? If yes, which one and what will be its mass?
(b) Calculate the mass of ammonia(NH3) that will be formed?
Solution 12.
Miscellaneous Exercise
1.From the equation for burning of hydrogen and oxygen
2H2 + O2  2H2O (Steam)
2H2O (Steam)
Write down the number of mole (or moles) of steam obtained from 0.5 moles of oxygen.
2.From the equation
3Cu + 8HNO3  3Cu (NO3)2+ 4H2O + 2NO
3Cu (NO3)2+ 4H2O + 2NO
(At.mass Cu=64, H=1, N=14,O=16)
Calculate:
(a) Mass of copper needed to react with 63g of HNO3
(b) Volume of nitric oxide at S.T.P. that can be collected.
Solution 2.
3.(a) Calculate the number of moles in 7g of nitrogen.
(b) What is the volume at S.T.P. of 7.1 g of chlorine?
(c) What is the mass of 56 cm3 of carbon monoxide at S.T.P?
Solution 3.
4.Some of the fertilizers are sodium nitrate NaNO3, ammonium sulphate (NH4)2SO4 and urea CO(NH2)2. Which of these contains the highest percentage of nitrogen?
Solution 4.
5.Water decomposes to O2 and H2 under suitable conditions as represented by the equation below:
2H2O 2H2+O2
2H2+O2
(a) If 2500 cm3 of H2 is produced, what volume of O2 is liberated at the same time and under the same conditions of temperature and pressure?
(b) The 2500 cm3 of H2 is subjected to 2 times increase in pressure (temp. remaining constant). What volume of H2 will now occupy?
(c) Taking the value of H2 calculated in 5(b), what changes must be made in Kelvin (absolute) temperature to return the volume to 2500 cm3 pressure remaining constant.
Solution 5.
6.Urea [CO(NH2)2] is an important nitrogeneous fertilizer. Urea is sold in 50 kg sacks. What mass of nitrogen is in one sack of urea?
Solution 6.
Molecular mass of urea=12 + 16+2(14+2) =60g
60g of urea contains nitrogen =28g
So, in 50g of urea, nitrogen present =23.33 g
50 kg of urea contains nitrogen=23.33kg
7.
Solution 7.
8.The following experiment was performed in order to determine the formula of a hydrocarbon. The hydrocarbon X is purified by fractional distillation.
0.145 g of X was heated with dry copper (II) oxide and 224 cm3 of carbon dioxide was collected at S.T.P.
(a) Which elements does X contain?
(b) What was the purpose of copper (II) oxide?
(c ) Calculate the empirical formula of X by the following steps:
(i) Calculate the number of moles of carbon dioxide gas.
(ii) Calculate the mass of carbon contained in this quantity of carbon dioxide and thus the mass of carbon in sample X.
(iii) Calculate the mass of hydrogen in sample X.
(iv) Deduce the ratio of atoms of each element in X (empirical formula).
Solution 8.
9.A compound is formed by 24g of X and 64g of oxygen. If atomic mass of X=12 and O=16, calculate the simplest formula of compound.
Solution 9.
Mass of X in the given compound =24g
Mass of oxygen in the given compound =64g
So total mass of the compound =24+64=88g
% of X in the compound = 24/88 100 = 27.3%
% of oxygen in the compound=64/88 100 =72.7%
Element % At. Mass Atomic ratio Simplest ratio
X 27.3 12 27.3/12=2.27 1
O 72.7 16 72.2/16=4.54 2
So simplest formula = XO2
10.A gas cylinder filled with hydrogen holds 5g of the gas. The same cylinder holds 85 g of gas X under same temperature and pressure. Calculate :
(a) Vapour density of gas X.
(b) Molecular weight of gas X.
Solution 10.
11.(a) When carbon dioxide is passed over red hot carbon, carbon monoxide is produced according to the equation :
CO2 + C  2CO
2CO
What volume of carbon monoxide at S.T.P. can be obtained from 3 g of carbon?
(b) 60 cm3 of oxygen was added to 24 cm3 of carbon monoxide and mixture ignited. Calculate:
(i) volume of oxygen used up and
(ii) Volume of carbon dioxide formed.
Solution 11.
12.
Solution 12.
13.
Solution 13.
(a) Number of molecules in 100cm3 of oxygen=Y
According to Avogadros law, Equal volumes of all gases under similar conditions of temperature and pressure contain equal number of molecules.Therefore ,number of molecules in 100 cm3 of nitrogen under the same conditions of temperature and pressure = Y
So, number of molecules in 50 cm3 of nitrogen under the same conditions of temperature and pressure =Y/100 50=Y/2
(b) (i) Empirical formula is the formula which tells about the simplest ratio of combining capacity of elements present in a compound.
(ii) The empirical formula is CH3(iii) The empirical formula mass for CH2O = 30
V.D = 30
Molecular formula mass = V.D 2 = 60
Hence, n =mol. Formula mass/empirical formula mass= 2
So, molecular formula = (CH2O)2 = C2H4O2
14.Ordinary chlorine gas has two isotopes 3517Cl and 3717Cl in the ratio of 3:1. Calculate the relative atomic mass of chlorine.
Solution 14.
The relative atomic mass of Cl = (35 x 3 + 1 x 37)/4=35.5 amu
15.Silicon (Si = 28) forms a compound with chlorine (Cl = 35.5) in which 5.6 g of silicon combines with 21.3 g of chlorine. Calculate the empirical formula of the compound.
Solution 15.
16.An acid of phoshorus has the following percentage composition; Phosphorus = 38.27%; hydrogen = 2.47 %; oxygen = 59.26 %. Find the empirical formula of the acid and its molecular formula, given that its relative molecular mass is 162.
Solution 16.
17.Calculate the mass of substance 'A' which in gaseous form occupies 10 litres at 270C and 700 mm pressure. The molecular mass of 'A' is 60.
Solution 17.
18.A gas cylinder can hold 1 kg of hydrogen at room temperature and pressure.
(a) What mass of carbon dioxide can it hold under similar conditions of temperature and pressure?
(b) If the number of molecules of hydrogen in the cylinder is X, calculate the number of carbon dioxide molecules in the cylinder. State the law that helped you to arrive at the above result
Solution 18.
So, mass of CO2 = 22 kg
(b) According to Avogadros law ,equal volumes of all gases under similar conditions of temperature and pressure contain equal number of molecules.
So, number of molecules of carbon dioxide in the cylinder =number of molecules of hydrogen in the cylinder=X
19.Following questions refer to one mole of chlorine gas.
(a) What is the volume occupied by this gas at S.T.P.?
(b) What will happen to volume of gas, if pressure is doubled?
(c) What volume will it occupy at 2730C?
(d) If the relative atomic mass of chlorine is 35.5, what will be the mass of 1 mole of chlorine gas?
19.Following questions refer to one mole of chlorine gas.
(a) What is the volume occupied by this gas at S.T.P.?
(b) What will happen to volume of gas, if pressure is doubled?
(c) What volume will it occupy at 2730C?
(d) If the relative atomic mass of chlorine is 35.5, what will be the mass of 1 mole of chlorine gas?
Solution 19.
(a) The volume occupied by 1 mole of chlorine = 22.4 litre
(b) Since PV=constant so, if pressure is doubled; the volume will become half i.e. 11.2 litres.
(c) V1/V2 = T1/T2
22.4/V2 =273/546
V2 = 44.8 litres
(d) Mass of 1 mole Cl2 gas =35.5 x 2 =71 g
20.(a) A hydrate of calcium sulphate CaSO4.xH2O contains 21% water of crystallisation. Find the value of x.
(b) What volume of hydrogen and oxygen measured at S.T.P. will be required to prepare 1.8 g of water.
(c) How much volume will be occupied by 2g of dry oxygen at 270C and 740 mm pressure?
(d) What would be the mass of CO2 occupying a volume of 44 litres at 250 C and 750 mm pressure?
(e) 1 g of a mixture of sodium chloride and sodium nitrate is dissolved in water. On adding silver nitrate solution, 1.435 g of AgCl is precipitated.
AgNO3 (aq) + NaCl (aq)  AgCl (s) + NaNO3
AgCl (s) + NaNO3
Calculate the precentage of NaCl in the mixture.
Solution 20.
21.
Solution 21.
22.
Solution 22.
(a) The molecular mass of (Mg(NO3)2.6H2O = 256.4 g
% of Oxygen = 12 x 16/256
= 75%
(b) The molecular mass of boron in Na2B4O7.10H2O = 382 g
% of B = 4 x 11/382 = 11.5%
23.A gas occupied 360 cm3 at 870C and 380 mm Hg pressure. If the mass of gas is 0.546 g, find its relative molecular mass.
Solution 23.
24.
Solution 24.
(a) 252 g of solid ammonium dichromate decomposes to give 152 g of solid chromium oxide, so the loss in mass in terms of solid formed = 100 g
Now, if 63 g ammonium dichromate is decomposed, the loss in mass would be = 100 x 63/252 = 25 g
(b) If 252 g of ammonium dichromate produces Cr2O3 = 152 g
So, 63 g ammonium dichromate will produce = 63 x 152/252
= 38 g
25.Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in oxygen to yield 12.8 g of sulphur dioxide gas as under :
25.Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in oxygen to yield 12.8 g of sulphur dioxide gas as under :
2H2S + 3O2  2H2O + 2SO2
2H2O + 2SO2
Calculate the volume of hydrogen sulphide at S.T.P. Also, calculate the volume of oxygen required at S.T.P. which will complete the combustion of hydrogen sulphide determined in (litres).
Solution 25.
26.Ammonia burns in oxygen and the combustion, in the presence of a catalyst. May be represented by 2NH3 + 2O2 ? 2NO + 3H2O
[H= 1, N= 14, O=16]
What mass of steam is produced when 1.5 g of nitrogen monoxide is formed?
Solution 26.
27.If a crop of wheat removes 20 kg of nitrogen per hectare of soil, what mass of the fertilizer, calcium nitrate Ca(NO3)2 would be required to replace the nitrogen in a 10 hectare field ?
Solution 27.
28.Concentrated nitric acid oxidises phosphorus to phosphoric acid according to the following equation:
P+ 5HNO3  H3PO4+ 5NO2 + H2O
H3PO4+ 5NO2 + H2O
If 6.2g of phosphorus was used in the reaction calculate:
(a) Number of moles of phosphorus taken and mass of phosphoric acid formed.
(b) mass of nitric acid will be consumed at the same time?
(c) The volume of steam produced at the same time if measured at 760 mm Hg pressure and 2730C?
Solution 28.
Since the pressure (760mm) remains constant , but the temperature (273+273)=546 is double, the volume of the steam also gets doubled
So,Volume of steam produced at 760mm Hg and 2730C = 4.48 × 2 = 8.96litre29.112 cm3 of a gaseous fluoride of phosphorus has a mass of 0.63 g. Calculate the relative molecular mass of the fluoride. If the molecule of the fluoride contains only one atom of phosphorus, then determine the formula of the phosphorus fluoride. [ F=19, P=31].
Solution 29.
30.Washing soda has formula Na2CO3.10H2O. What mass of anhydrous sodium carbonate is left when all the water of crystallization is expelled by heating 57.2 g of washing soda?
Solution 30.
31.(a)
(b) A metal M forms a volatile chloride containing 65.5% chlorine. If the density of the chloride relative to hydrogen is 162.5, find the molecular formula of the chloride (M = 56).
Solution 31.
32.
Solution 32.
V1/V2 = n1/n2
So, no. of moles of Cl = x/2 (since V is directly proportional to n)
No. of moles of NH3 = x
No. of moles of SO2 = x/4
This is because of Avogadros law which states Equal volumes of all gases, under similar conditions of temperature and pressure, contain equal number of molecules.
So, 20 litre nitrogen contains x moleculesSo, 10 litre of chlorine will contain = x × 10/20=x/2 mols.
And 20 litre of ammonia will also contain =x molecules
And 5 litre of sulphur dioxide will contain = x × 5/20 = x/4 mols.
33.The reaction: 4N2O + CH4
Solution 33.
34.Samples of the gases O2, N2, CO2 and CO under the same conditions of temperature and pressure contain the same number of molecules x. The molecules of oxygen occupy V litres and have a mass of 8 g under the same of temperature and pressure
What is the volume occupied by:
(a) x molecules of N2
(b) 3x molecules of CO
(c) What is the mass of CO2 in grams?
(d) In answering the above questions, which law have you used?
Solution 34.
(a) Volume of O2 = V
Since O2 and N2 have same no. of molecules = x
so, the volume of N2 = V
(b) 3x molecules means 3V volume of CO
(c) 32 g oxygen is contained in = 44 g of CO2
So, 8 g oxygen is contained in = 44 x 8/32 = 11 g
(d) Avogadro’s law is used in the above questions.
35.The percentage composition of sodium phosphate as determined by analysis is 42.1% sodium, 18.9% phosphorus and 39% oxygen. Find the empirical formula of the compound?
Solution 35.
(a) 444 g is the molecular formula of (NH4)2 PtCl6
% of Pt = (195/444) x 100 = 43.91% or 44%
(b) simple ratio of Na = 42.1/23 = 1.83 = 3
simple ratio of P = 18.9/31 = 0.609 = 1
simple ratio of O = 39/16 = 2.43 = 4
So, the empirical formula is Na3PO4
36.What volume of oxygen is required to burn completely a mixture of 22.4 dm3 of methane and 11.2 dm3 of hydrogen into carbon dioxide and steam?
CH4 + 2O2  CO2 + 2H2O
CO2 + 2H2O
2H2 + O2  2H2O
2H2O
Solution 36.
37.The gases hydrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, sulphur dioxide and chlorine are arranged in order of their increasing relative molecular masses. Given 8 g of each gas at S.T.P., which gas will contain the least number of molecules and which gas the most?
Solution 37.
According to Avogadros law:
Equal volumes of all gases, under similar conditions of temperature and pressure ,contain equal number of molecules.
38.10 g of a mixture of sodium chloride and anhydrous sodium sulphate is dissolved in water. An excess of barium chloride solution is added and 6.99 g of barium sulphate is precipitated according to the equation given below:
Na2SO4 + BaCl2  BaSO4 + 2NaCl
BaSO4 + 2NaCl
Calculate the percentage of sodium sulphate in the original mixture.
Solution 38.
39.When heated, potassium permanganate decomposes according to the following equation :
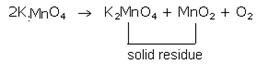
(a) Some potassium permanganate was heated in the test tube. After collecting one litre of oxygen at room temperature, it was found that the test tube had undergone a loss in mass of 1.32 g. If one litre of hydrogen under the same conditions of temperature and pressure has a mass of 0.0825 g, calculate the relative molecular mass of oxygen.
(b) Given that the molecular mass of potassium permanganate is 158. What volume of oxygen (measured at room temperature) would be obtained by the complete decomposition of 15.8 g of potassium permanganate? (Molar volume at room temperature is 24 litres)
Solution 39.
40.(a) A flask contains 3.2 g of sulphur dioxide. Calculate the following:
(i) The moles of sulphur dioxide present in the flask.
(ii) The number of molecules of sulphur dioxide present in the flask.
(iii) The volume occupied by 3.2 g of sulphur dioxide at S.T.P.
(S= 32, O= 16)
(b) An Experiment showed that in a lead chloride solution, 6.21 g of lead is combined with 4.26 g of chlorine. What is the empirical formula of this chlorine? (Pb = 207; Cl = 35.5)
Solution 40.
41.The volume of gases A, B, C and D are in the ratio, 1 : 2 : 2 : 4 under the same conditions of temperature and pressure .
(i) Which sample of gas contains the maximum number of molecules?
(ii) If the temperature and pressure of gas A are kept constant, then what will happen to the volume of A when the number of molecules is doubled?
(iii)If this ratio of gas volume refers to the reactants and products of a reaction, which gas law is being observed?
(iv)If the volume of A is actually 5.6 dm3 at S.T.P., calculate the number of molecules in the actual Volume of D at S.T.P. (Avogadro's number is 6  1023).
1023).
(v) Using your answer from (iv), state the mass of D if the gas is dinitrogen oxide (N2O)
Solution 41.
(i) D contains the maximum number of molecules because volume is directly proportional to the number of molecules.
(ii) The volume will become double because volume is directly proportional to the no. of molecules at constant temperature and pressure.
V1/V2 = n1/n2V1/V2 = n1/2n1
So, V2 = 2V1
(iii) Gay lussac’s law of combining volume is being observed.
(iv) The volume of D = 5.6 4 = 22.4 dm3, so the number of molecules = 6 x 1023 because according to mole concept 22.4 litre volume at STP has = 6 x 10 23 molecules
(v) No. of moles of D = 1 because volume is 22.4 litre
so, mass of N2O = 1 44 = 44 g
42.The equation given below relate the manufacture of sodium carbonate (molecular weight of Na2CO3 = 106).
1. NaCl+NH3+ CO2 + H2O NaHCO3+NH4Cl
NaHCO3+NH4Cl
2. 2NaHCO3  Na2CO3+H2O + CO2
Na2CO3+H2O + CO2
Equations (1) and (2) are based on the production of 21.2 g of sodium carbonate.
(a) What mass of sodium hydrogen carbonate must be heated to give 21.2 g of sodium carbonate?
(b) To produce the mass of sodium hydrogen carbonate calculate in (a), what volume of carbon dioxide, measured at S.T.P. would be required?
Solution 42.
43.A sample of ammonium nitrate when heated yields 8.96 litres of steam (measure at S.T.P.)
NH4NO3 N2O + 2H2O
N2O + 2H2O
(i) What volume of dinitrogen oxide is produced at the same time as 8.96 litres of steam?
(ii) What mass of ammonium nitrate should be heated to produce 8.96 litres of steam? (Relative molecular mass of ammonium nitrate is 80)
(iii) Determine the percentage of oxygen in ammonium nitrate (O = 16).
Solution 43.
44.
Solution 44.
(a) Element % Atomic mass Atomic ratio Simple ratio
K 47.9 39 1.22 2
Be 5.5 9 0.6 1
F 46.6 19 2.45 4
so, empirical formula is K2BeF4
(b) 3CuO + 2NH3 → 3Cu + 3H2O + N2
3 V 2 V 3 V 1V
3 x 80 g of CuO reacts with = 2 x 22.4 litre of NH3
so, 120 g of CuO will react with = 2x 22.4 x 120/80 x 3
= 22.4 litres
45.(a) Calculate the number of moles and the number of molecules present in 1.4 g of ethylene gas. What is the volume occupied by the same amount of ethylene?
(b) What is the vapour density of ethylene?
Solution 45.
(a) The molecular mass of ethylene(C2H4) is 28 g
No. of moles = 1.4/28 = 0.05 moles
No. of molecules = 6.023 x1023 x 0.05 = 3 x 1022 molecules
Volume = 22.4 x 0.05 = 1.12 litres
(b) Molecular mass = 2 X V.D
S0, V.D = 28/2 = 14
46.(a) Calculate the percentage of sodium in sodium aluminium fluoride (Na3AlF6) correct to the nearest whole number.
(F = 19; Na =23; Al = 27)
(b) 560 ml of carbon monoxide is mixed with 500 ml of oxygen and ignited. The chemical equation for the reaction is as follows:
2CO + O2  2CO2
2CO2
Calculate the volume of oxygen used and carbon dioxide formed in the above reaction.
Solution 46.
47.a. A gas cylinder of capacity of 20 dm3 is filled with gas X the mass of which is 10 g. When the same cylinder is filled with hydrogen gas at the same temperature and pressure the mass of the hydrogen is 2 g, hence the relative molecular mass of the gas is:
i. 5
ii. 10
iii. 15
iv. 20
b.
i. Calcium carbide is used for the artificial ripening of fruits. Actually the fruit ripens because of the heat evolved while calcium carbide reacts with moisture. During this reaction calcium hydroxide and acetylene gas is formed. If 200 cm3 of acetylene is formed from a certain mass of calcium carbide, find the volume of oxygen required and carbon dioxide formed during the complete combustion. The combustion reaction can be represented as below.
ii. A gaseous compound of nitrogen and hydrogen contains 12.5% hydrogen by mass. Find molecular formula of the compound if its relative molecular mass is 37. [N = 14, H = 1].
c.
i. A gas cylinder contains 24 x 1024 molecules of nitrogen gas. If Avogadro's number is 6 x 1023 and the relative atomic mass of nitrogen is 14, calculate :
1. Mass of nitrogen gas in the cylinder
2. Volume of nitrogen at STP in dm3.
(ii) Commercial sodium hydroxide weighing 30g has some sodium chloride in it. The Mixture on dissolving in water and subsequent treatment with excess silver nitrate solution formed a precipitate weighing 14.3 g. What is the percentage of sodium chloride in the commercial sample of sodium hydroxide? The equation for the reaction is
[Relative molecular mass of NaCl = 58; AgCl = 143]
(iii) A certain gas 'X' occupies a volume of 100 cm3 at S.T.P. and weighs 0.5 g. Find its relative molecular mass
Solution 47.
48.a.
i. LPG stands for liquefied petroleum gas. Varieties of LPG are marketed including a mixture of propane (60%) and butane (40%). If 10 litre of this mixture is burnt, find the total volume of carbon dioxide gas added to the atmosphere. Combustion reactions can be represented as :
s
ii. Calculate the percentage of nitrogen and oxygen in ammonium nitrate. [Relative molecular mass of ammonium nitrate is 80, H = 1, N = 14, O = 16].
b. 4.5 moles of calcium carbonate are reacted with dilute hydrochloric acid.
i. Write the equation for the reaction.
ii. What is the mass of 4.5 moles of calcium carbonate? (Relative molecular mass of calcium carbonate is 100)
iii. What is the volume of carbon dioxide liberated at STP?
iv. What mass of calcium chloride is formed? (Relative molecular mass of calcium chloride is 111).
v. How many moles of HCl are used in this reaction?
Solution 48.
49.a.
i. Calculate the volume of 320 g of SO2 at STP. (Atomic mass: S = 32 and O = 16).
ii. State Gay-Lussac's Law of combining volumes.
iii. Calculate the volume of oxygen required for the complete combustion of 8.8 g of propane (C3H8). (Atomic mass: C = 12, O = 16, H = I, Molar Volume = 22.4 dm3 at stp.)
b.
i. An organic compound with vapour density = 94 contains C = 12.67%, H = 2.13%, and Br = 85.11%. Find the molecular formula. [Atomic mass : C = 12, H = 1, Br = 80]
ii. Calculate the mass of:
1. 1022 atoms of sulphur.
2. 0.1 mole of carbon dioxide.
[Atomic mass : S = 32, C = 12 and O = 16 and
Avogadro's Number = 6 x 1023]
Solution 49.
50.a. Concentrated nitric acid oxidises phosphorus to phosphoric acid according to the following equation:
If 9.3 g of phosphorus was used in the reaction, calculate :
i. Number of moles of phosphorus taken.
ii. The mass of phosphoric acid formed.
iii. The volume of nitrogen dioxide produced at STP.
b.
i. 67.2 litres of hydrogen combines with 44.8 litres of nitrogen to form ammonia under specific conditions as:
Calculate the volume of ammonia produced. What is the other substance, if any, that remains in the resultant mixture?
ii. The mass of 5.6 dm3 of a certain gas at STP is 12.0 g. Calculate the relative molecular mass of the gas.
iii. Find the total percentage of Magnesium in magnesium nitrate crystals, Mg(NO3)2-6H2O.
[Mg = 24, N = 14, 0 = 16 and H = 1]
Solution 50.

51.a.
i. What volume of oxygen is required to burn completely 90 dm3 of butane under similar conditions of temperature and pressure?
ii. The vapour density of a gas is 8. What would be the volume occupied by 24.0 g of the gas at STP?
iii. A vessel contains X number of molecules of hydrogen gas at a certain temperature and pressure. How many molecules of nitrogen gas would be present in the same vessel under the same conditions of temperature and pressure?
b. O2 is evolved by heating KClO3 using MnO2 as a catalyst.
i. Calculate the mass of KClO3 required to produce 6.72 litre of O2 at STP.
[atomic masses of K = 39, Cl = 35.5, 0 = 16].
ii. Calculate the number of moles of oxygen present in the above volume and also the number of molecules.
iii. Calculate the volume occupied by 0.01 mole of CO2 at STP.
Solution 51.

52.a.
i. Oxygen oxidises ethyne to carbon dioxide and water as shown by the equation:
What volume of ethyne gas at s.t.p. is require to produce 8.4 dm3 of carbon dioxide at STP [H = 1, C = 12, 0 = 16]
ii. A compound made up of two elements X and Y has an empirical formula X2Y. If the atomic weight of X is 10 and that of Y is 5 and the compound has a vapour density (V.D.) 25, find its molecular formula.
b. A cylinder contains 68 g of Ammonia gas at STP
i. What is the volume occupied by this gas?
ii. How many moles of ammonia are present in the cylinder?
iii. How many molecules of ammonia are present in the cylinder?
Solution 52.
53.
Solution 53.
54.
Solution 54.
55.
Solution 55.
56.
Solution 56.
(a) (i) element % atomic mass at. ratio simple ratio
C 14.4 12 1.2 1
H 1.2 1 1.2 1
Cl 84.5 35.5 2.38 2
Empirical formula = CHCl2
(ii) Empirical formula mass = 12+1+71= 84 g
Since molecular mass = 168 so, n = 2
so, molecular formula = (CHCl2)2 = C2H2Cl4
(b) (i) C + 2H2SO4 → CO2 + 2H2O + 2SO2
1 V 2 V 1 V 2 V
196 g of H2SO4 is required to oxidized = 12 g C
So, 49 g will be required to oxidise = 49 x 12/196 = 3 g
(ii) 196 g of H2SO4 occupies volume = 2 x 22.4 litres
So, 49 g H2SO4 will occupy = 2 x 22.4 x 49/196 = 11.2 litre
i.e. volume of SO2 = 11.2 litre
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps








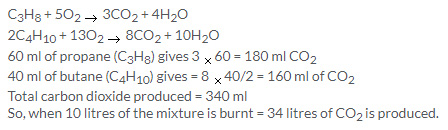










































































Comments
Post a Comment
This site is all about helping you kids study smart because for Gen Z, studying "hard" is not enough. If you feel there is any way I could improve my posts or if you have any random suggestion that might help make this more kid friendly, please don't hesitate to drop in a comment!
Be sure to check back for my response if you've asked me a question or requested a clarification through the comment section because I do make every effort to reply to your comments here.